How does it work
History of Gait Modification Therapy
19th Century – Emergence of Formal Study
- Pioneers – Introduction of biomechanics in rehab; studies on posture and locomotion begin
- Military rehab – gain analysis used to help wounded soldiers recover mobility
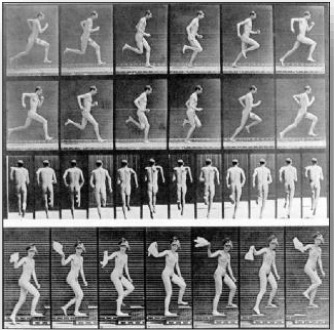
20th Century
- Early – Birth of Physical Therapy
- Polio – Rise in gait modification techniques to assist patients
- Prosthetics and Orthotics – Development of assistive devices and braces to improve walking patterns
- Mid – Scientific and Technological Advancements
- Laboratory Gait Analysis – Introduction of force plates and video analysis to assess gait
- Rehab programs – Gait retraining incorporated into physical therapy and occupational therapy
- Late – Biomechanics and Customized Therapy
- Computerized Motion Capture
- Personalized Intervention
21st Century – Sophisticated Analysis, AI and Intelligent Devices in Gait Therapy
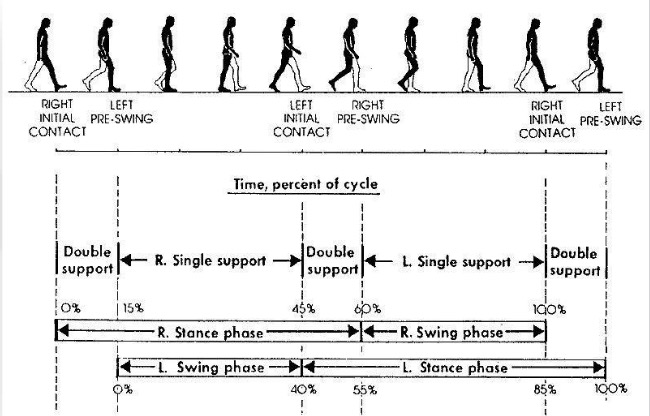
Gait Modification Therapy – How does it work?
Improves Movement
- Optimizes foot/ground contact to reduce and normalize forces acting on the ankle, knee and hip
- Normalizes joint loads, allowing more physiologic joint function
- More physiologic joint function leads to more natural coordination of muscle activity
Neuromuscular Training
- Subtle instability provides a powerful signal for muscle recruitment optimization
- Improves gait speed and symmetry
- Improves balance and stability
Relieves Pain
- Changing force through joints and soft tissues
- Unloading painful structures, loading non-painful structures
- Pain inhibition through spinal cord reflexes
- Presynaptic inhibition of pain neurons in the spinal cord by mechanoreceptors
- Pain inhibition from higher cortical pathways
- Descending inhibition from the cortex
- Serotonergic pathway
- Enkephalinergic pathway
- Noradreneric pathway
- Descending inhibition from the cortex
Utilizes advanced physical and computerized gait analysis to quantify:
• Painful regions of the joint
• Center of Pressure
• Stride Length
• Stride Speed
• Single Leg Stand Time
• 100+ additional data points
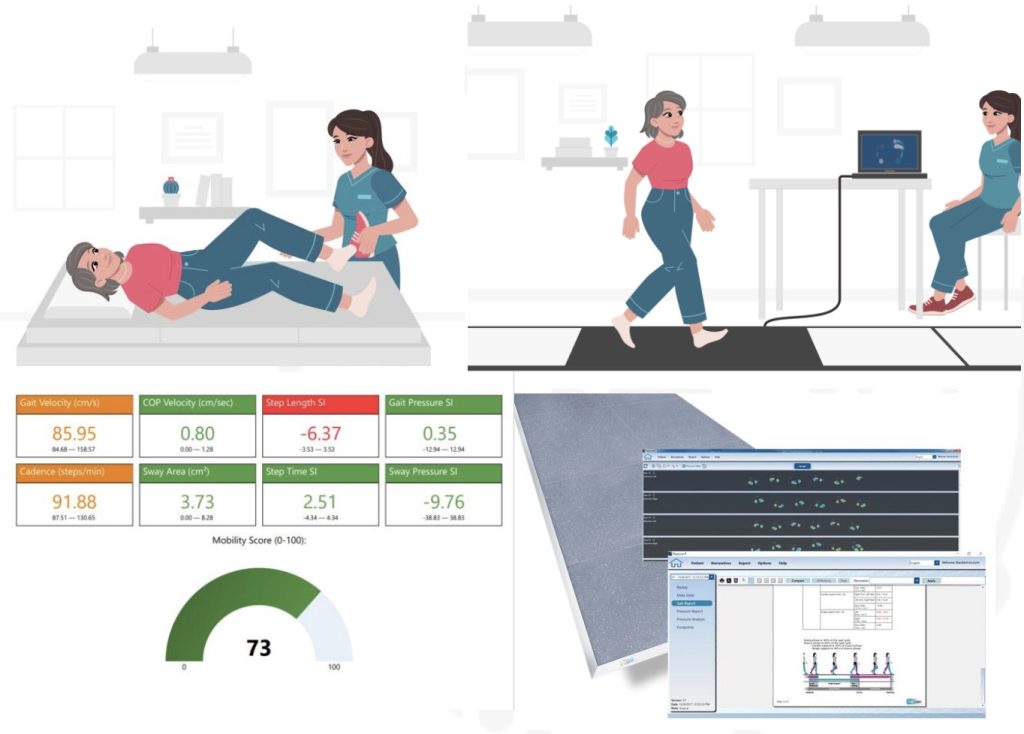

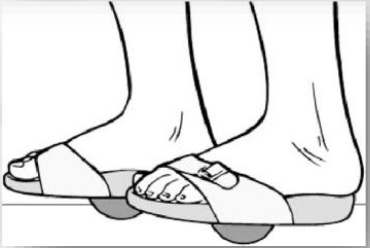
Information guides adjustment of patent-pending, contoured outsole specific to patients needs
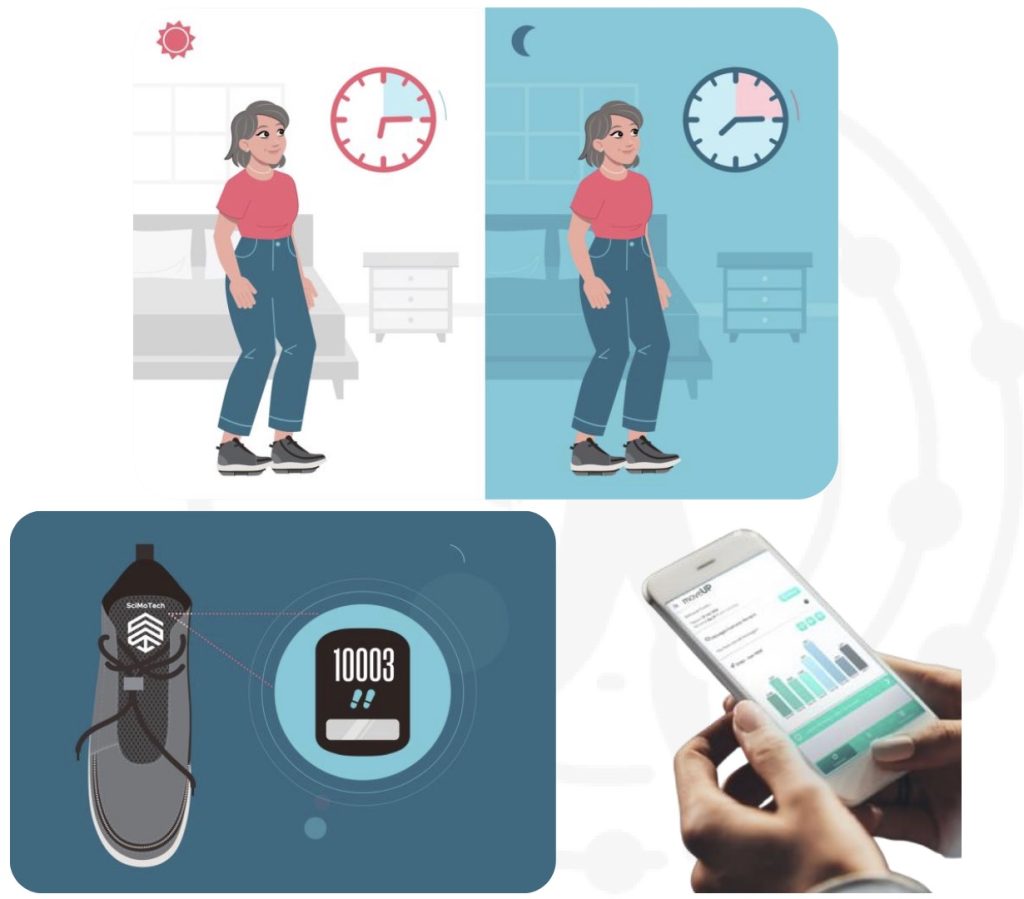
Process results in a personalized, prescription footworn biomechanical device to be worn by the patient at home as part of a therapy protocol
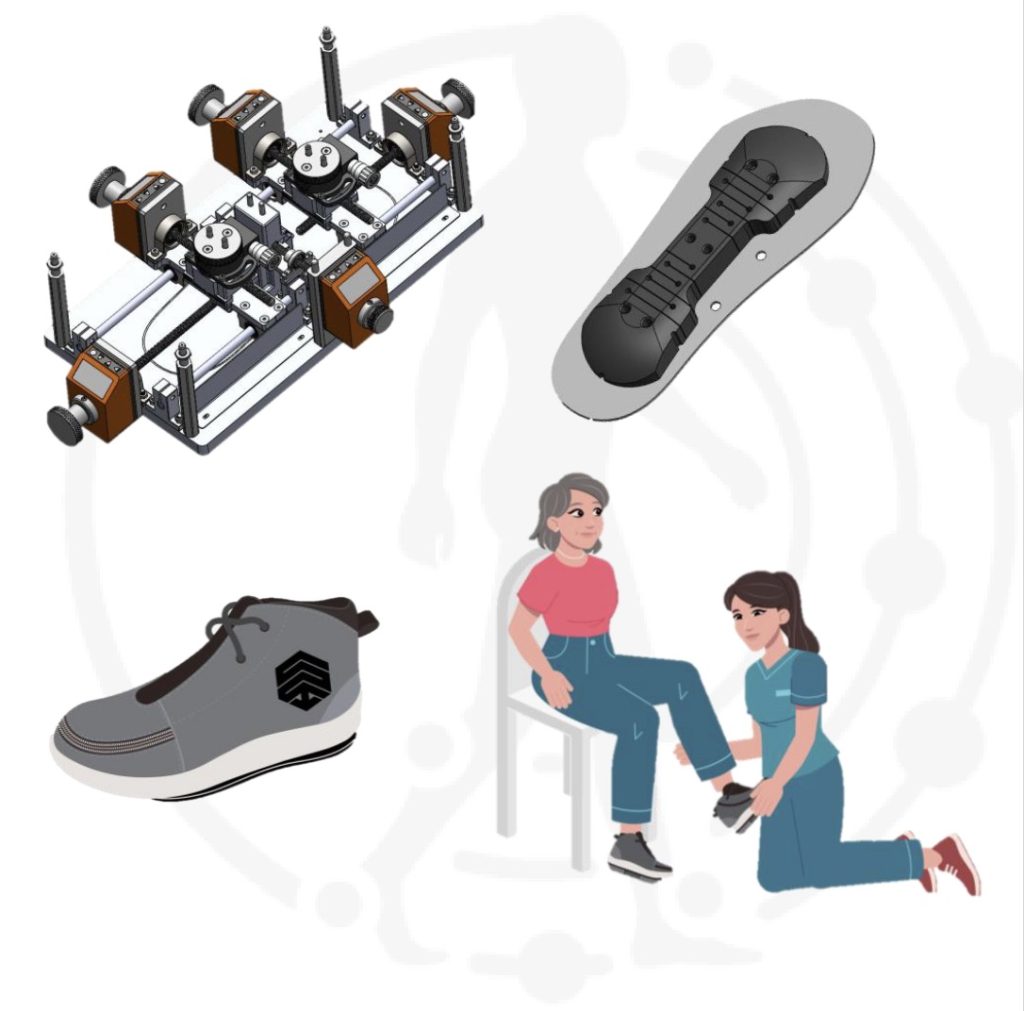
Patients utilize the therapy by wearing the footwear in the home, for 15–30 minutes per day during normal daily activities
Patients’ activity and progress is recorded and tracked via sensors and remote monitoring

Provides patients an opportunity to:
- Avoid and/or delay surgery for joint pain
- Reduce or eliminate prescription medication for pain
- Improve quality of life and mobility
- Keep up with loved ones’ activities – don’t get left behind
- Improve night pain for better sleep and recovery
- Enjoy the convenience of at-home therapy
- Apply SciMoTech therapy in the comfort of one’s own home
- Avoid bridges burned
- Completely non-invasive, non-surgical therapy
